Alternative Page With Proper Canonical Tag
Canonical (rel=canonical) – We have often heard this term in on-page SEO . But to know more about it, let us discuss the canonical tag and its application in SEO.
Let us take an example of a website that sells Mobile Phones which has different pages with the same content. Therefore, it might have different URLs for the same page such as
- smartphone.com/apple
- smartphone.com/brand/apple
- smartphone.com/apple/utm_campaign
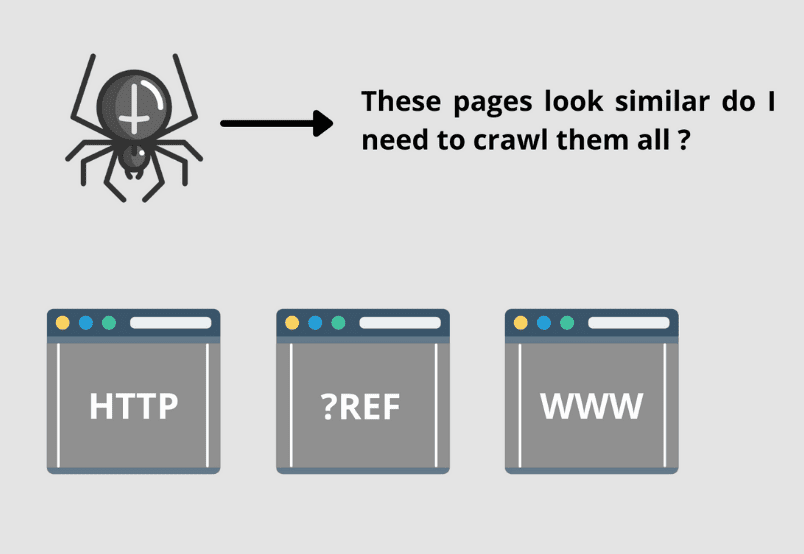
All the three pages have similar content or are exact replicas of each other. Such pages may be created due to some changes in the backend. These URLs could be used for tracking purposes or created due to different categories in the top navigation.
However, having so many URLs for the same page can leave Google incredibly confused about which URL to rank in the SERP.
(Depending on the signals, Google picks up one URL that it feels is the best version and ranks it.)
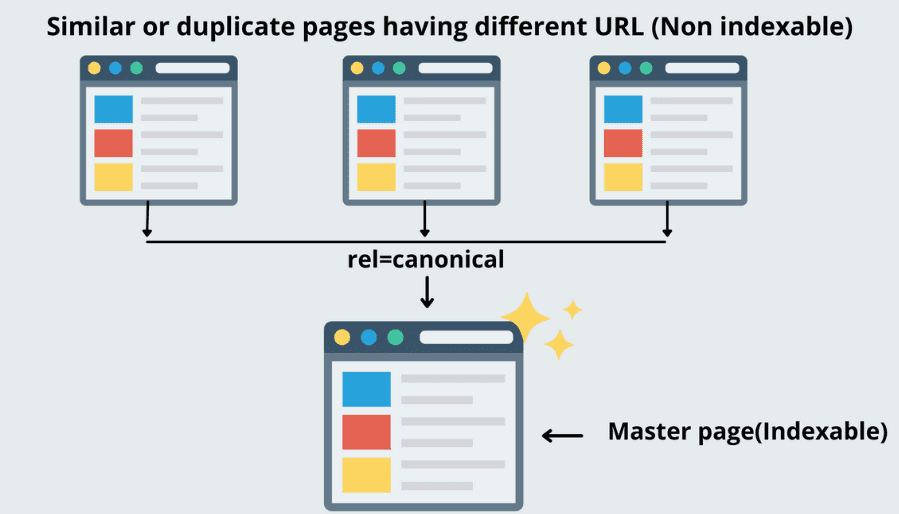
Google is not always accurate and might end up choosing the incorrect URL. This makes it necessary to let Google understand which page and URL to rank in the SERP and which to ignore. Here is where canonical tags come in the picture.
What are canonical tags?
A canonical tag (rel = canonical) in SEO is a piece of HTML code that helps Google to rank a particular page from a group of similar/duplicate pages.
Let us follow our previous example of a website selling mobile phones to further elaborate on the term. Suppose you want to indicate to Google that "smartphone.com/apple" is your main page that you want to rank for. You will simply put a canonical tag on all the other duplicate pages.
Why are canonical tags important in SEO optimization?
Whether you are an SEO agency or an SEO professional, canonicalization should be on your list of activities within On-Page SEO optimization . Now, let us find out what makes canonical tags so important in SEO?
-
Saves crawl budget
By specifying a canonical tag, you indicate to Google which URL to index and rank out of various versions of the page. This saves valuable time for the spider that crawls your website. The crawler, also known as a web spider, needs not waste time crawling pages that have been canonicalized. In this way, the web spider can reach other important URLs and content on your website and saves your crawl budget.
-
Proper allocation of Link Juice
Using canonical tags ensures that the link juice is passed to the correct version of the page. If you have different pages with similar content, Google evenly distributes link juice to all these pages. By specifying a canonical tag, you let Google decide the page you want to give importance and rank in SERP. Google then passes all the link juice to the important page, ignoring all the duplicate pages. This ensures that there is a proper allocation of link juice on your website.
-
Ensures relevant URLs rank for queries
Canonical tags help ensure that relevant URLs rank for keywords. The last thing you want is two URLs of your website competing against each other for the same keyword on SERPs. By using rel=canonical, you can avoid this situation. Make sure you specify the proper canonical URL that you want Google to index and rank in the canonical tag HTML code.
-
Canonical tags make Google's job easy
If you have a huge website with numerous URLs, it becomes tedious for Google to crawl all these URLs. When coupled with the confusion of duplicate pages and different variations of the same page, Google will have a hard time crawling and indexing these URLs. But, it is your website that will suffer the consequences. So, in order to make Google's job easy, you need to specify proper canonical tags on all the pages. This makes sure Google crawls and indexes the correct pages.
Canonical Tags vs. 301 Redirects
301 Redirects can be understood as a permanent redirect done from one page URL to another. All the users are redirected to the new mentioned page in case of 301 redirects . For example, if you 301 redirect Page A to Page B, the users will automatically land to page B only. However, in the case of canonical tags, when you canonicalize Page A to Page B, users can visit both pages A and B.
The reason why canonical tags are compared with 301 redirects is that 301 redirects usually pass link equity (PageRank, Authority, etc.). On the other hand, canonical tags may sometimes not pass the link equity and get avoided by the search engine if there are multiple issues within the link.
How to Implement Canonical Tag?
The following methods will help you comprehend how to implement canonical tags to your URLs:
-
HTML Tag
HTML tags, also known as the 'rel=canonical tag,' are one of the easiest ways to help specify a canonical URL. To implement the tag, simply add the given code to the <head> section of a duplicate page.
Code: <link rel="canonical" href="https://xyz.com/canonical-page/" />
For example, you have an eCommerce store that sells shoes. Further, you want to make https://mystore.com/shoes/ the canonical URL, as the same page is also accessible through other URLs such as https://mystore.com/offers/shoes . Therefore add the given canonical tag to get accurate results:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://mystore.com/shoes/" />
-
HTTP Header
HTTP headers are useful for adding canonical tags to a page that does not have a <head> section, such as pdf files and documents. In such scenarios, you will have to use HTTP headers to set canonicals. The HTTP headers can also be used on standard web pages.
Let suppose we have a pdf file for this blog uploaded on a website URL for which we want to add the tag. Here is how to do it:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/pdf
Link: <https://xyz.com/blog/canonical-tags/>; rel="canonical"
-
Sitemap
You must be thinking, what is sitemap ? A sitemap is a file that contains information about the web pages, videos, and other files present on your website. It also specifies the relationship of different files with one another.
Search engines like Google suggest that non-canonical pages must not be added to the sitemap. This is because search engines generally view the web pages listed in a sitemap as recommended canonicals. However, Google clearly mentions that it does not necessarily consider URLs in sitemaps as canonicals.
- 301 Redirect
301 Redirects provides an excellent way to divert a website's traffic from a duplicate URL to the canonical version. Let us suppose that your webpage can be accessed through these URLs:
- xyz.com
- xyz.com/index.php
- xyz.com/home/
Select one of them as a canonical tag and redirect the other URLs there. The same goes for both secured and unsecured versions of your website. If the canonical version of xyz.com is https://xyz.com , the redirects can be as follows:
- http://xyz.com/
- http://www.xyz.com/
- https://www.xyz.com/
Canonical Tag Syntax
The syntax of Canonical Tag is <link rel="canonical" href="URL" />
The code has two important components
- rel="canonical"
- href="URL"
link rel="canonical"
rel means relationship. Therefore, we define the relationship of the link as canonical.
href = "URL"
href tells the link's destination. Here is where you put the URL that you want Google to index and rank. This is also called the canonical URL.
Coming back to our example, our smartphone website has the following URLs
- smartphone.com/apple
- smartphone.com/brand/apple
- smartphone.com/apple/utm_campaign
You want Google to only index and rank "smartphone.com/apple" out of these URLs. All you must do is put a canonical tag on the duplicate pages.
This means you put a canonical tag on both URLs
"smartphone.com/brand/apple" and "smartphone.com/apple/utm_campaign".
The canonical tag will be as follows
<link rel="canonical" href="https://smartphone.com/apple/" />
Simple. This tells Google that "smartphone.com/apple" is your main version and it should index and rank it, ignoring the other duplicate pages.
Note : The canonical tag should always be placed in the <head> section of the page.
What is a self-referential canonical tag?
A self-referential canonical tag is a tag that is defined on the main version of the page; irrespective of duplicate pages elsewhere.
This means, even if your page does not have other similar pages with duplicate content , you still put a canonical tag on that page. This is also known as self canonical.
-
Example of self canonical
Let us take our website selling mobile phones for instance.
A self-referential (aka self-referencing) tag refers to adding a canonical tag to the main page "smartphone.com/apple". You can add this canonical tag even if there are no other duplicate pages of this URL (i.e. "smartphone.com/brand/apple" and "smartphone.com/apple/utm_campaign" do not exist).
"smartphone.com/apple" page will have a self canonical tag as follows:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://smartphone.com/apple/" />
The syntax for self-referential canonical tag is the same. The only difference between the two is that a self-referential tag is placed within the head section of the main page.
-
Google on self-referencing canonicals
In one of his webmaster hangout sessions, Google's John Mueller said that Google recommends putting self-referential canonical tags on all pages. He pointed out that sometimes many different variations of URLs get created due to a mixture of upper and lower case or www and non-www variants.
However, using self-referencing canonicals directs Google towards the proper URL to index and rank.
Hence, adding self-referential canonical tags on all the pages is now considered as a best practice in SEO .
What is a cross-domain canonical tag?
A canonical tag given on a page that is not on your domain, but has content similar to a page on your website, is called a cross-domain canonical tag.
For example, you have a blog page "abc.com". You decide to syndicate your blog articles. Syndicating basically means re-posting your blog posts on other domains as a guest. The purpose of this process is to share your content on popular websites to increase your reach.
But one problem that occurs in this process is that the same content which is on your website is used on other websites. This could lead to Google flagging it as a duplicate content . In order to avoid this scenario, we use the cross-domain canonical tag.
If you have re-published your article on a popular website like Medium, this page should have a cross-domain canonical tag stating that the main version of the page comes from abc.com.
The cross-domain canonical tag will be as follows
<link rel="canonical" href="https://abc.com/article" />
This measure tells Google that the main article is on abc.com and has been re-published on Medium.
The syntax for the cross-domain canonical tag is the same. The difference here is that this canonical tag is added to the page where you have re-published your content. This measure is called cross-domain as you are putting a canonical tag on a page that is not on your domain.
Note : All the syndication websites might not include a cross-domain canonical tag, despite multiple requests. You must play the risk game in these situations.
Canonical Tags Best Practices
Canonical tags can effectively enhance the SEO-friendliness of your web pages. Hence, they must be strategically used to achieve better search engine rankings. Here are some of the essential things you should consider while implementing canonical tags :
1. Always Use Accurate Domain Version
You may use different protocols such as SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) to secure your page or domain from unauthorized access and hacks. In general, websites with SSL protocols have 'HTTPS' added to their URLs, and websites that do not have any security protocol start with 'HTTP.'
So if you have switched your website to SSL, ensure that you do not declare any non-SSL URLs in your canonical tags. It may lead to confusion, and you may not get the expected results on the search engine.
For secured domains , use the following version of canonical tags:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://xyz.com/sample-page/" />
For unsecured domains , use the following version of canonical tags:
<link rel="canonical" href="http://xyz.com/sample-page/" />
2. Make Sure to Add Canonical Tags to Your Home Page
Adding relevant canonical tags to your home page is a valuable step for your SEO optimization process. It helps search engines make a distinction about the master copy of the specified webpage. Many times, various internet sites copy your website content and generate different copies of the same content.
In that case, the search engine gets confused about which one is the original page that should be ranked. When you use a canonical tag to point to the original URL, the search engine will not mistake it for another website, and you will get the desired results.
3. Utilise Self-Referential Canonical Tags
Self-referential canonical tags are the tags that point towards themselves so that search engines can get clear information on which page needs to be indexed. URLs sometimes have different variations, which can cause confusion, and therefore using a self-referential canonical tag can prevent this issue.
Modern content management systems have an automatic system to add self-referencing canonical tags. However, if you are using a customized CMS, you may have to add the tags yourself. For instance, if the URL of a page is https://xyz.com/sample-page , the self-referencing canonical tag for the page would be <link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/sample-page" /> .
4. Keep it Straightforward
Always keep things simple and straightforward while adding a canonical tag to your webpage. Often, search engines avoid picking a tag if they cannot interpret the given information correctly.
If you are canonicalizing page A to page B, simply add the tag and leave it there. You do not have to again canonicalize page B to page A. Doing so can send mixed signals to the search engine, and it may prefer not to use the tag at all. Also, avoid chaining canonical tags with one another as it may go against your website.
5. Make Use of Near-Duplicates Pages
Most people think of canonical tags as exact duplicates of the page being referred to. However, this is not true. You may add canonical tags on pages that are near-duplicates or have almost similar content. If not implemented with caution, the search engine may ignore the tag.
But if you are using the tags for similar pages, such as the page of a product that only differs by location, currency, or some small product attribute, then you can add a canonical tag to that page without any doubt.
6. Write Lowercase URLs and Add Single URL Per Page
Search engines typically treat lowercase and uppercase URLs as two different URLs. Therefore, ensure to force the lowercase URLs on your server. Then utilize lowercase URLs for the canonical tags. Furthermore, never add multiple canonical tags on your webpage. The search engine will most likely ignore the tags if more than a single tag is present on the page.
How to audit canonical tags and issues on a website?
-
Manual checks
If you have a small website and want to manually check the presence of a proper canonical tag on your pages, perform a manual check. Follow the steps mentioned below to do the same:
- Go to your page
- Press Ctrl+U to view the source code of the page
- Search for "canonical"
- You can find the canonical tag code in the <head> section
- Make sure the canonical tag is implemented correctly
-
Using Tools
Checking manually becomes tedious if you have a huge number of pages on your website. For this, you can utilize various crawling tools for checking canonical tag implementation.
Ahrefs has its own site audit tool which gives you all the information you need about canonical tags on your website.
You can also use Screaming Frog for auditing canonical tags which is much more detailed and resourceful. Just open the Screaming Frog Spider software and make sure you check "canonicals" in the Crawl settings. Once the crawl is complete, you can view all the details under "Canonicals" tabs.
Different canonical issues and ways to fix them
You may come across some issues when you inspect a website for canonical tags. At first, these issues may seem small, but they can significantly hurt your SEO. Here's a list of such canonical tag issues and ways to fix them:
-
Canonical tags point to 4XX or 5XX pages
This error occurs when your canonical tags point to a 4XX or 5XX status code page. It is likely that for different reasons, some of the pages on your website are deleted. In such cases, make sure that you remove the canonical tags on all the pages that point to such 4XX or 5XX pages. You can either replace the canonical URL with the working 200 status code page or delete the canonical URL that points to pages that do not exist anymore.
-
Non-canonical URL in hreflang
This issue arises when pages contain non-canonical URLs in their hreflang implementation. If you have hreflang implemented on your website, make sure you add the proper canonical URL in the hreflang code. If you don't do so, the search engine will be confused as to which pages to consider for ranking. If you come across non-canonical URLs in hreflang, immediately replace them with the proper canonical URL.
-
Internal Links Pointing to Non-Canonical Version
This is a common problem that mostly occurs when a new page replaces an old one. In such cases, a canonical tag is put on the old page that points to the new page. However, site owners forget to change the URL in the footer links and top navigation. This results in the internal links pointing towards the old non-canonical page.
To fix this, make sure you replace all the links in the footer or top navigation with the URL of the new canonical version of the page. This will ensure that your canonical page is strong and properly linked.
-
Sitemap Contains Non-Canonical URLs
This issue occurs when all the non-canonical pages are present in the sitemap. Google recommends that non-canonical URLs be excluded from the sitemap as this would confuse the search engines as to which page to index and rank. Make sure that only the canonical version of the page is included in the sitemap. This will ensure that the right version of the page is ranked in the Google Search Engine Results Page (SERP).
-
Duplicate Pages Without Canonical Tags
An issue may arise if one or more duplicate pages exist on the internet and there is not any specified canonical version provided for the web page. As there will not be a canonical tag present, the search engine will identify the most appropriate version for the search query. However, it might not be the same version or URL that you want to be indexed.
To fix this problem, review all the duplicates of the page. Then, select a version that you want to index in search results and add a self-referencing canonical tag to it. Also, make sure to specify this as a canonical version amongst all other duplicate versions.
-
Non-Canonical Page Described as a Canonical Page
If more than one page specifies a canonical URL that is also canonicalized to a different webpage, an error may occur. In such a case, a canonical chain gets built where page A is linked to page B, and page B is linked to page C.
The formation of these chains adds a level of complexity and the search engines may misinterpret the information and avoid using specified canonical. To counter this problem, you can replace non-canonical links with direct links in the canonical tags of affected pages.
-
Non-Canonical Page Gets More Organic Traffic
A warning may trigger if more than one non-canonical page appears in the search engine result page and receive higher organic search traffic. This may happen if your canonical tags are not set up correctly or the search engine does not accept the added canonicals.
To fix this issue, recheck if all your rel=canonical tags are implemented correctly on the web pages. You can also leverage the URL Inspection tool by Google to check if your specified canonical URL is considered canonical or not.
Common mistakes to avoid when using canonical tags
Canonicalization can sometimes be very confusing. If not done right, you can lose your rankings as well. We've collated a list of common mistakes that occur when using canonical tags. This will help you implement canonical tags without errors.
-
Canonicalized URLs blocked in robots.txt file
If canonicalized URLs are blocked in robots.txt, the search engine bot won't crawl them. Due to this, the canonical tag present on these pages won't be visible to the search engine bot. This kind of mistake can hurt your SEO as the link juice from these pages won't be passed to the canonical page. Do not block your canonicalized pages in the robots.txt file.
-
Noindex tag present on canonicalized pages
By putting a noindex tag on your canonicalized pages, you prevent Google from indexing them. This is not a good practice when using canonical tags. Canonicalization is implemented when you want Google to know you have different URLs for the same page, but you want a specific page to be ranked in the SERP. As a best practice, don't use both noindex and canonical tags together.
-
Canonicalizing all pages in the paginated series to the first page
Pagination is breaking down your main page into a set of pages. Many e-commerce websites implement pagination on their category pages. Here's an example:
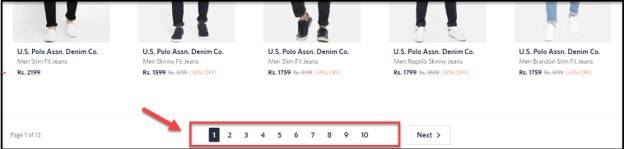
One common mistake that SEO professionals make is that they canonicalize all pages (page2, page3, page4, and so on) to the main page (page 1). Google's John Mueller has stated that this is a bad canonicalization practice. Here's his take on this:
"The main thing to avoid, since this post is about Canonicalization, is to use the rel=canonical on page 2 pointing to page 1. Page 2 isn't equivalent to page 1, so the rel=canonical like that would be incorrect."
It is also a good practice to use 'rel=next' and 'rel=prev' tags for your paginated pages as Bing still supports them. This will help search engines understand the correct order of pages.
Conclusion
Canonical tag is a very important part of code in relation to on-page SEO techniques . Google has stated multiple times that it encourages the use of canonical tags on all the pages.
However, you need to avoid the presence of duplicate content on your websites as much as possible. But we do understand that for large websites, sometimes doing so is difficult. Hence, duplicate pages are created due to various reasons.
We advise you to use proper canonicals on all pages with different versions and duplicate content. The best practice would be to make sure that you put a self-referential tag on all your pages to avoid confusion.
The canonical tag is just a simple one-line code, but it works wonders.
Let us know in the comments section if you have faced any such canonicalization issues and how have you dealt with them. Also, let us know if you have any doubts regarding canonical tags.
Popular Searches
SEO Company in India | Best SEO Company in Bangalore | Best SEO Company in Delhi | SEO Company in Mumbai | SEO Consultants in Mumbai | Digital Marketing Services in India | SEO Services in India | Ecommerce SEO Services | Website Audit Services | Google Penalty Recovery Services | Local SEO Services in India | PPC Services in India | ASO Services in India | Conversion Rate Optimization Services in India | Link Building India | Content Marketing Services | Rankbrain Update | List of HTTP Status Codes | History of Google | Types of Digital Marketing | List of Search Engines | What is Off-Page SEO | What is PPC | Organic Traffic | What is YouTube SEO
Alternative Page With Proper Canonical Tag
Source: https://www.infidigit.com/blog/canonical-tags/
Posted by: tillerdank1972.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Alternative Page With Proper Canonical Tag"
Post a Comment